
Firewall vs Antivirus: Key Differences and Why You May Need Both
When it comes to the plethora of security tools designed to protect us from the myriads of cyber threats, there often exists a considerable amount of confusion around firewall vs antivirus and their respective differences in coverage.
In this article, we we’ll break down these two critical components of cybersecurity, highlighting their distinct roles and how they work together to provide comprehensive protection against a wide range of cyber threats. Understanding these tools will empower users to make informed decisions about our personal data security.
Understanding Firewalls
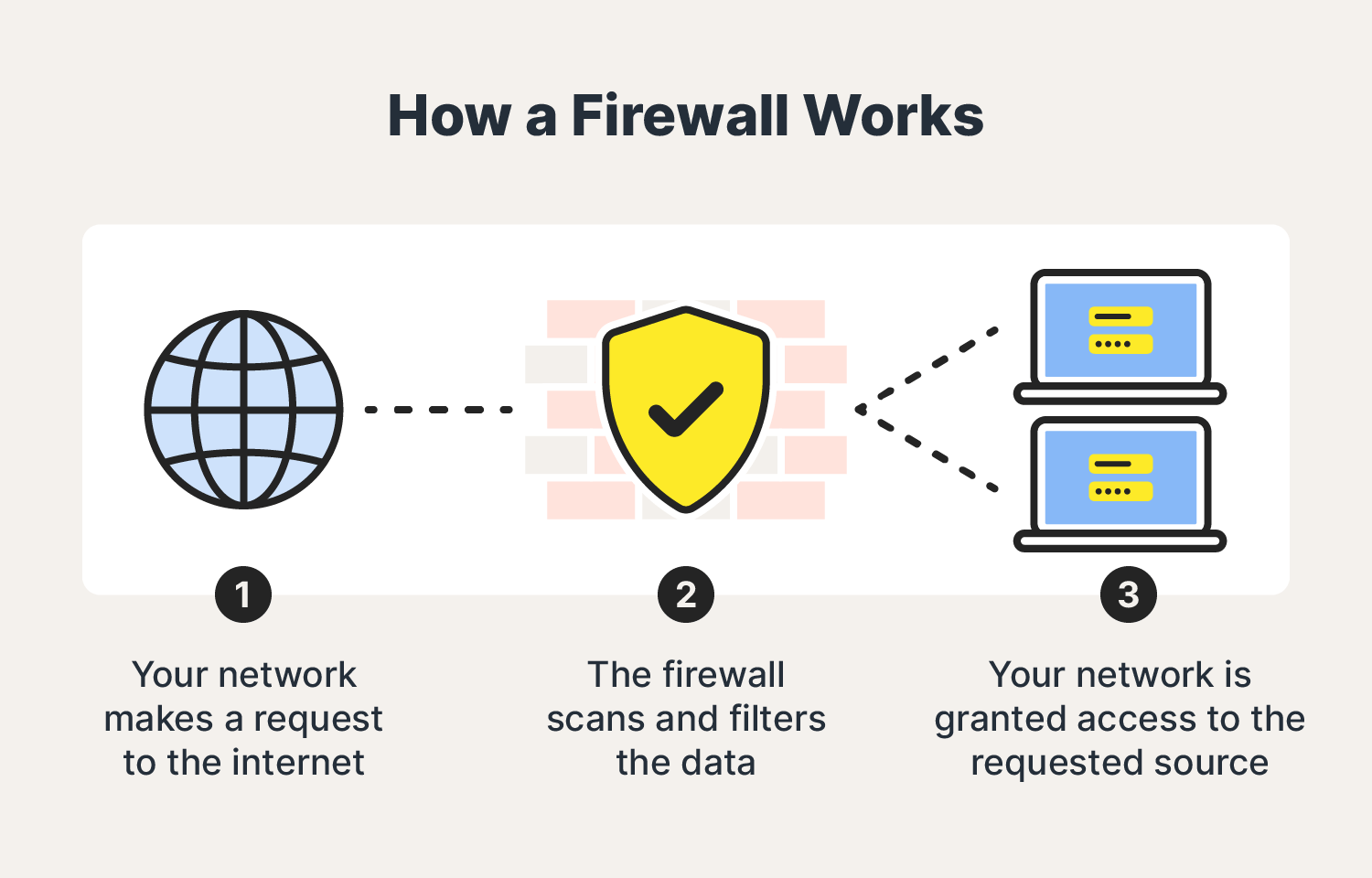
A firewall acts as a safeguard between your device and the external world, including the internet. It monitors and screens outgoing and incoming network traffic to ensure its safety before it reaches your device. There are two kinds of firewalls: software and hardware. A software firewall defends against digital intrusions, while a hardware firewall stops others from physically accessing your device, such as using a USB stick when your device is inactive.
Firewalls are utilized in personal and enterprise settings. Many devices, including Mac, Windows, and Linux computers, come with built-in firewalls. Some popular firewall brands are Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, Check Point, SonicWall, Juniper Networks, and Barracuda Networks. Each brand offers advanced features and robust security solutions tailored to diverse organizational needs.
Pros and cons of using firewall software
At a high level, firewall is a barrier between your network and potential threats to your security. Firewall offers a great flexibility to cybersecurity, where admins can set specific rules, resources, accesses, and VPNs. Firewall also filters and monitors traffic to provide real-time pings on potential security issues, breaches, unusual activity, and malware.

Firewalls might not detect or prevent security threats that work at the application or endpoint level since their capability is limited to monitoring and controlling network-level traffic. Firewalls often represent a significant expense for small businesses, both in terms of acquisition and ongoing maintenance, and their correct setup demands technical expertise for proper configuration.
Antivirus
Antivirus is a specialized software or application engineered to guard against malicious software originating from the internet. This includes viruses, worms, spyware, and trojans that can cause significant damage to your data and privacy. This software works by conducting a three-step process. First, it discovers the potential threat. Then, it recognizes the specific nature of the threat. Finally, it eliminates the threat. It’s important to note that antivirus software can address both external and internal threats. However, its application is strictly limited to software and does not extend to hardware. Some commonly known antivirus software programs include McAfee, Norton, and BullGuard.
Pros and cons of antivirus software
Antivirus software holds a host of positive applications both similar and in contrast to firewall security. Antivirus focuses on monitoring your system files constantly to detect potential threats. We’re talking worms, viruses, and ransomware. Alongside monitoring software, antivirus can proactively target threats through system performance monitoring, safe browsing, and scanning.

Utilizing an antivirus application consumes significant memory and hard disk resources. This heavy usage can lead to a noticeable decrease in the computer’s performance. Additionally, the process of conducting scans can sometimes result in delays within the network. Many antivirus applications tend to overwhelm users with advertisements, suggesting upgrades for enhanced protection. Although a few of these offers might be useful, most are primarily designed to generate revenue or persuade users to switch to a paid software version.
Unpacking the core differences of firewall vs. antivirus
The main difference between firewalls and antivirus software lies in their primary functions and security approaches.

Core functionality
A firewall acts as a filter for your network traffic, aiming to block the entry of infected files, malware, and viruses to prevent cybercriminals from taking advantage of vulnerabilities. On the other hand, antivirus software’s purpose is to identify, neutralize, and eliminate malware and viruses already present in your computer or network by scrutinizing files and isolating potential threats.
A firewall is designed to handle external threats, while antivirus software is equipped to tackle both external and internal threats. Within firewalls, the potential for counterattacks exists, notably through IP Spoofing and routing attacks. On the other hand, once antivirus software successfully removes malware, no further counterattacks can occur.
Setting up and maintaining a firewall can be challenging and time-consuming, especially for larger networks or companies with a wide range of users and devices. Meanwhile, programming the antivirus is comparatively easier than configuring the firewall.
Why antivirus and firewall security are both essential for cybersecurity
While there are major differences between firewall and antivirus software approaches and you may be inclined to choose one, the smartest security actually combines both to create a robust defense framework.

With firewall as a barrier between your org and the external world of access, antivirus software can scan your computer for threats that have already been sent, downloaded, or found on your system. Combined, these two systems offer a layered security approach that prevents initial access, offers consistent monitoring, and blocks malicious network access.
Defense in Depth
Defense in Depth is a security strategy that employs multiple layers of defense mechanisms to protect information and systems. If one layer fails, additional layers continue to provide protection.

This layered defense then addresses different types of threats: unauthorized network access, threats within the system, and evolving malicious acts. When one layer of security is breached, you have backup. If a trojan horse is able to jump your firewall and plant a virus, your antivirus will detect the threat immediately. This makes security breaches more difficult, and if they do go through, easier to identify and mitigate. defensive measures, and having multiple layers ensures that your security can evolve as well.
Combining firewalls and antivirus software as part of a DID strategy provides a more robust and resilient security framework, ensuring comprehensive protection against a wide range of cyber threats.
Distilled
When deciding on security measures for your business, you might wonder if having a firewall and antivirus protection is necessary. The answer is definitively yes. Each serves a unique purpose in safeguarding your digital environment. By leveraging the combined strengths of these tools, you can maximize the protection of your critical data and systems, giving you greater peace of mind and safeguarding your organization’s digital assets.